Common Health Issues Detected During Work Permit Medical Check-Ups

Work permit medical check-ups are a vital part of ensuring the health and safety of foreign workers, as well as the general public. These mandatory screenings serve as a preventive measure to detect common health issues that could affect an individual’s ability to work, or potentially spread communicable diseases within the workplace and community.
In this article, we’ll explore some of the most common health issues detected during a medical check-up for work permit applicants and discuss their implications.
Tuberculosis (TB)
One of the primary health issues screened during a medical check-up for work permit applicants is tuberculosis (TB). This airborne disease poses a significant public health risk, especially in workplaces where employees work in close proximity to one another.
During the screening process, chest X-rays are typically conducted to detect any signs of active TB in the lungs. If TB is detected, the worker will need to undergo further treatment and may be temporarily ineligible for work until the condition is managed.
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is another condition frequently detected during work permit medical check-ups. It is a viral infection that can cause both acute and chronic liver disease. The virus is spread through contact with infected blood or bodily fluids, making it a concern for industries where employees might be exposed to such risks, such as healthcare or manual labor jobs.
Blood tests are used to screen for hepatitis B during the medical check-up process. If an individual is found to be infected, they are usually referred for treatment and monitoring to prevent the disease from progressing.
In some cases, this condition may temporarily delay the work permit approval depending on the severity of the infection and its implications for the individual’s health and work capacity.
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), such as syphilis, are also screened during the medical check-up for work permit holders. These infections can have serious long-term health consequences if left untreated, including reproductive issues, organ damage, and increased risk of contracting other infections such as HIV. Early detection is crucial in preventing the spread of STIs and ensuring that workers receive appropriate medical treatment.
Routine screening for syphilis and other STIs is often conducted through blood tests. Detecting and addressing these infections during the medical check-up ensures that the worker receives timely treatment, reducing the likelihood of complications and improving overall health outcomes.
Mental Health Issues
Although physical health checks are the main focus of work permit medical check-ups, mental health issues are also increasingly being identified as a concern. Anxiety, depression, and stress are common issues among migrant workers who may be dealing with the pressure of adjusting to a new country, demanding work schedules, and being away from their families.
In some cases, medical professionals conducting the work permit check-up may refer workers for mental health evaluation and support if they display symptoms of psychological distress. Identifying these issues early allows for proper intervention, helping to ensure that the worker can cope with the challenges of their new environment and perform their job effectively.
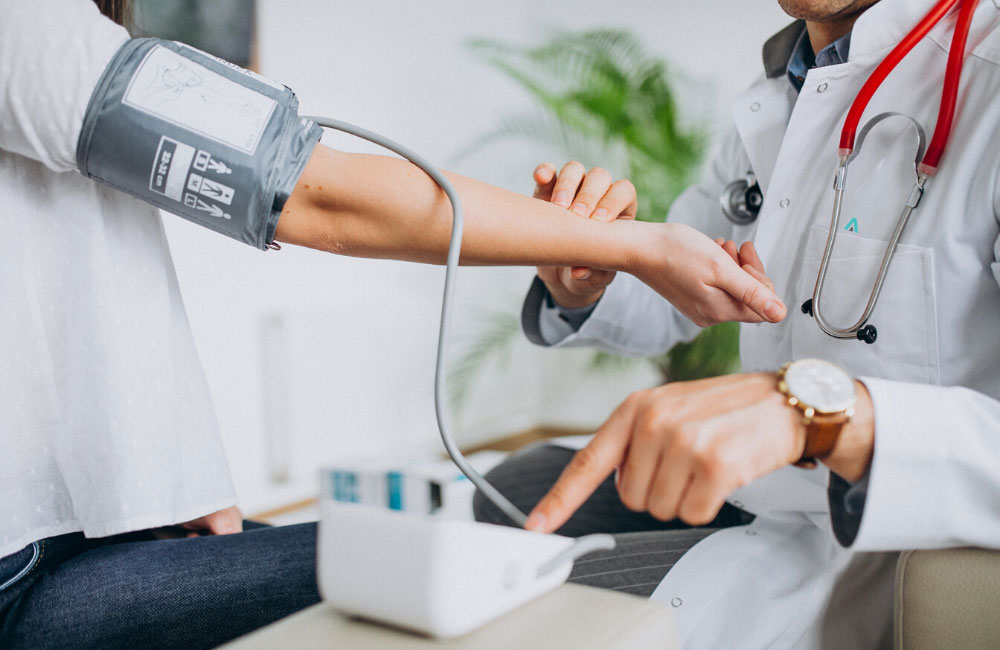
Hypertension and Cardiovascular Risks
High blood pressure (hypertension) and other cardiovascular risks are frequently detected during work permit medical check-ups. These conditions are particularly prevalent among older workers or individuals with unhealthy lifestyles. Left unmanaged, hypertension can lead to severe complications such as heart attacks or strokes, posing significant risks to both the worker and their ability to perform labor-intensive jobs.
During the check-up, blood pressure is measured to assess the worker’s cardiovascular health. If elevated blood pressure is detected, the worker may be advised to seek further evaluation and management to prevent future health problems. Workplaces with physically demanding tasks need to ensure that their employees are fit for the job, and managing cardiovascular risks is an important part of that process.
Diabetes
Diabetes is another common health condition that may be identified during a medical check-up for work permit applicants. Blood glucose levels are typically tested to detect signs of diabetes, especially for individuals who may be at higher risk due to factors such as age, weight, or family history. Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to complications such as nerve damage, kidney disease, and even vision loss, which can significantly impact a worker’s performance and quality of life.
Conclusion
Work permit medical check-ups play a crucial role in safeguarding the health of foreign workers and the communities they integrate into. By detecting common health issues such as tuberculosis, hepatitis B, sexually transmitted infections, and chronic conditions like hypertension and diabetes, these screenings help ensure that workers receive the medical attention they need before they begin their employment.